What is type 1 diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition where the sugar or glucose levels in the blood rise very high, but this glucose cannot move into body cells. For every cell in the human body, energy is required for all its processes and glucose or sugar is the source of this energy. Normally, when we eat food, it gets metabolized into glucose and other nutrients that enter blood stream. This glucose is the fuel for our body cells and it will be able to move into the body cells only in the presence of a hormone called insulin. In type 1 diabetes, either the insulin is not produced or is produced in low amount, thus impairing blood sugar regulation, causing retention of sugar in the blood stream itself.
Type 1 diabetes is also known as insulin-dependent diabetes. As the name infers, type 1 diabetes is Type 1 Diabetes a state totally dependent on insulin levels, and develops when there is little or no insulin production in the body. This form of diabetes represents up to 5% of total diabetic population, mostly seen in children or young adults, so it is also called ‘juvenile diabetes’.
Development of type 1 diabetes is closely linked to family history and often runs in families. It cannot be prevented but can be managed by taking appropriate diet, regular exercise, and glucose monitoring, and insulin supplementation.
Until scientists have perfected ways to better treat and possibly even prevent or cure type 1 diabetes, parents can help their children lead happier, healthier lives by giving constant encouragement, arming themselves with diabetes information, and making sure their children eat properly, exercise, and stay on top of blood sugar control every day. Doing so will enable kids to do all the things that other children do while helping them grow up to be healthy, well-adjusted, productive adults.
What are the causes of type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes happens when the pancreas in the body stops producing insulin which is essential for absorption of blood glucose into body cells. It is caused due to damage of the insulin producing cells by the immune system of the person’s own body. The immune system mistakenly recognizes the β cells of pancreas (insulin producing cells) as harmful and destroys them; thereby the pancreas cannot make insulin anymore. Normally, cell destruction takes place over years but symptoms appear rather quickly and by the time of diagnosis, when most of cells would have already been destroyed.
An exact cause of this specific immune-mediated destruction remains unknown. Most often, type 1 diabetes can be genetic putting anyone at 6% risk of type 1 diabetes when a parent or siblings are diabetic, whereas otherwise the risk is under 0.5%. When people are born, the genes are hereditary transferred from their biological parents. Many genes are involved in making a person susceptible to type 1 diabetes or offering protection from type 1 diabetes.
Most likely reason for this form of diabetes is a combination of genetic susceptibility and environmental factors. Various environmental factors that can be responsible for type 1 diabetes include – certain viruses, bacteria and other factors like cow’s milk. These act as triggers to the immune response in one’s body to destruct the β cells.
What are the Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is a condition that develops quickly along with rapid onset and progression of symptoms, over a few days or weeks, especially in children. For older adults, this could be slower and symptoms develop over a few months.
It is important to recognize the symptoms while the disease is in early stages as quarter of the people have an acute complication, ketoacidosis by the time of diagnosis.
There are 4 typical symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes
Thirst - as sugar gets build up in blood, kidneys try to flush this off through urine but along with sugar water is also lost form the body causing dehydration
- Feeling thirsty even after having a bottle or two of water
- Repeatedly waking during nights to drink water
Thinner – although sugar is accumulated in blood, cells will not be able to take this glucose for energy and body tries to derive energy by breaking down muscle proteins, therefore causing muscle loss and reduced weight
- Losing weight even on eating sufficient food, without any reason
Toilet – while kidney tries to filter and eliminate sugar, water also comes out through urine leading to increased urination
- If you notice short gaps between going to the toilet, and urinating during the nights which was not usual before, you may suspect diabetes
- Bedwetting in a child who has been dry previously
Tired – lack of insulin causes reduced energy for body cells making the person feel tired
- If a child or person who is normally active starts finding difficulty in doing certain things or physical activities
Other common symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes:
- Feeling very hungry – even while eating enough
- Having a blurry vision
- Itchiness near genitals, or infections
- Slowed wound healing
- Irritability and other mood changes
When the disease is not evaluated and managed in early stages, this could lead to extremely high blood sugar levels resulting in a medical emergency called diabetic ketoacidosis, and the individual shows following signs and symptoms
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fruity smell from the breath
- A high body temperature
- Stomach pain
This condition needs urgent medical attention and hospital admission.
Treating Type 1 Diabetes
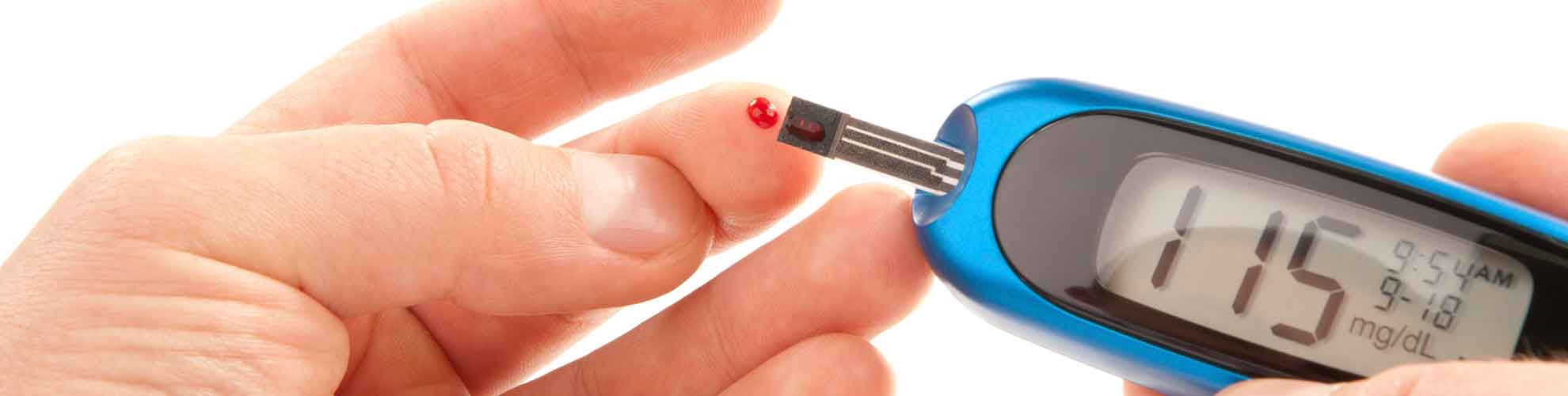
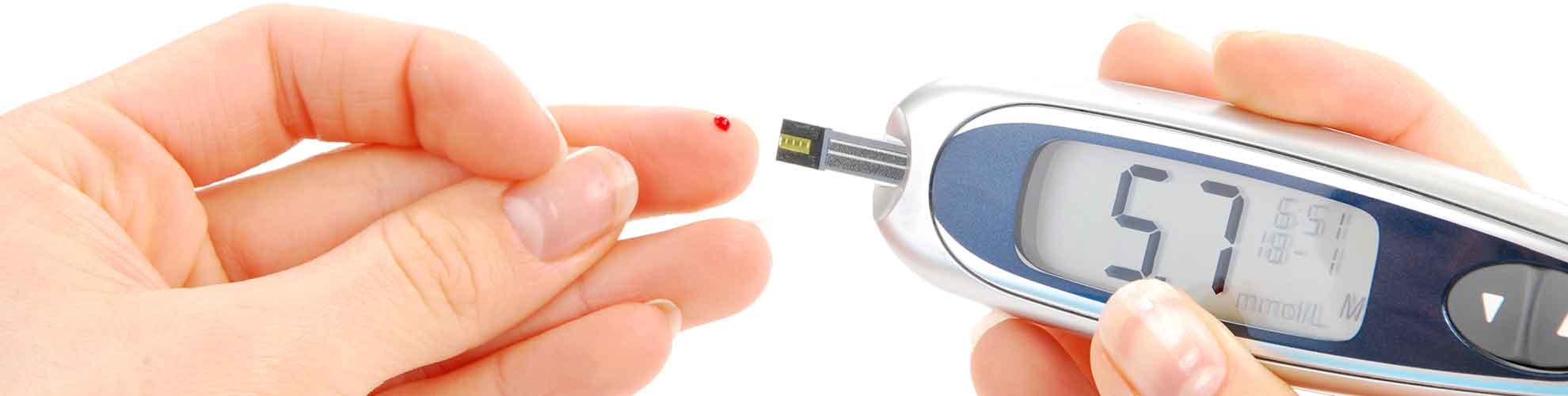
An important part of the treatment for type 1 diabetes is to make sure that your blood sugar level is as stable as possible. Often, you’ll need to check your blood glucose levels during the day, whether at home, work or school, with the finger prick blood test. Depending on the type of insulin treatment you’re taking, you may have to repeat this test four or more times a day. Your diabetes expert will talk to you about your ideal blood glucose level, and will prescribe the right diet and exercise regime for you. Don’t delay an expert consult if you notice any of the symptoms of type 1 diabetes.
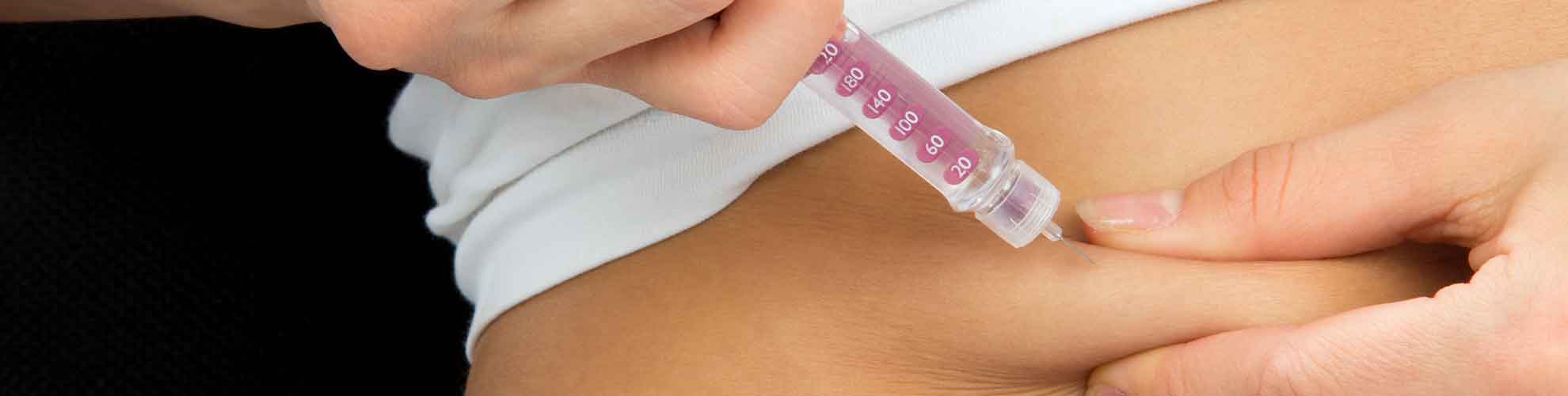
Type 1 diabetes is primarily caused by the lack of insulin in the body, so insulin supplementation is a key component of type 1 diabetes treatment plan
- If disease is diagnosed newly, the person might need to visit the doctor more for until the individual requirements for insulin are accurately determined and ensured to be followed
- As the sugar levels get stabilized the requirement for doctor visits may be eventually reduced
- The dose and type of insulin that the person may require will be determined by the physician considering a variety of factors
- Healthy eating and regular exercise are equally important in type 1 diabetes treatment that will help the person maintain a healthy weight and decrease the likelihood of complications
- Discuss with your doctor regarding special instructions for how the exercise or diet pattern can affect the sugar levels and how can they adjust the insulin injections
- People with type 1 diabetes also need to learn how to count the amount of carbohydrates in their food and how to adjust insulin doses accordingly
- Additionally, self-monitoring of glucose levels is another critical part of Type 1 diabetes management and includes checking the blood sugar by yourself using glucometer
- Your doctor or diabetic counselor suggests you
- How many times per day you will need to check the glucose levels
- what can be done if you have abnormal readings
- You should discuss about your HbA1c target and mostly for type 1 diabetics, it is ≤5%
- Your doctor or diabetic counselor suggests you
- If you are observed to have any complications, you might be prescribed with medicines for managing the complications such as eye, kidney, heart disease, gum problems, hearing problems
- If you smoke, quit smoking as it can increase your risk for complications
- Taking good care of your feet to prevent foot complications
- Check for signs of numbness, any problem with skin, bones (feet and also legs) and talk with your doctor if you see anything abnormal
- Other necessary tests that you might need to get done to ensure a good health with diabetes are:
| SR. NO | TESTSFREQUENCY OF TESTS | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Blood pressure | At least once a year (140/80 or lower) |
| 2 | HbA1c test | Controlled sugar levels – every 6 months Uncontrolled sugar – every 3 months |
| 3 | Lipid profile | Once a year |
| 4 | Kidney tests | Once a year |
| 5 | Thorough eye check up | Once a year |
| 6 | Dental cleaning and check up | Every 6 months |
Following the treatment plan can help a person stay healthy, but it’s not a cure for diabetes. Currently there’s no cure for diabetes, so people with type 1 diabetes will need treatment for the rest of their lives. However, with the help of the right diabetes experts, you can stick to the plan, stay healthy and avoid diabetes problems later. Apollo Sugar has just the experts and packages for you to live healthy with type 1 diabetes.